New Publication: Unlocking the Future of Food Safety with Blockchain Technology

The University of Thessaly, coordinator of the ALLIANCE project, has led a literature review study titled "Digital Transformation of Food Supply Chain Management Using Blockchain: A Systematic Literature Review Towards Food Safety and Traceability", recently published on the Business & Information Systems Engineering Journal.
This publication explores how Blockchain technology, alongside tools like Artificial Intelligence, is reshaping the future of Food Supply Chains (FSCs) by tackling one of their most pressing challenges: ensuring trust, traceability, and safety across complex, global networks.
The globalization of contemporary Food Supply Chains (FSCs) has introduced complexities involving multiple actors, food product transportation, and diverse information. Traditional information systems in FSCs face challenges in ensuring transparency and traceability due to the inherent complexities of multi-actor involvement, global transportation, and diverse information, making it difficult to ascertain product origin and processes, exacerbating issues such as food loss, safety concerns, and financial hazards.
Blockchain technology, in conjunction with ancillary technologies, offers potential solutions to these challenges. This systematic literature review endeavors to comprehensively explore the multifaceted dimensions of blockchain’s role in FSC management, with an emphasis on food safety and traceability, across six thematic areas, each guided by distinct criteria. These areas include general information, FSC application, factors of blockchain adoption, blockchain platform, ancillary technologies, and the related impact of blockchain adoption.
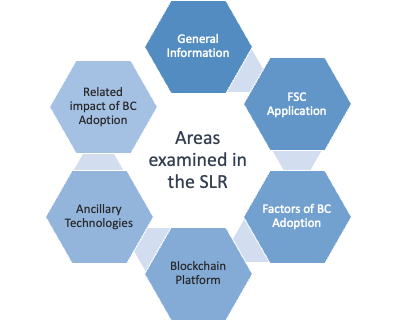
From the 2097 documents found, 122 full-text articles were assessed, and 61 were included and classified in this study based on criteria. These criteria underscore blockchain's capacity for transparency, resilience, and sustainability in FSCs.
The results indicate that blockchain's integration within the FSCs has unveiled a tapestry of possibilities and considerations that underpin its transformative potential in business systems. Blockchain’s inherent traits of transparency and immutability can enhance traceability, mitigate food fraud, and facilitate consumer trust, reshaping the information system’s implementation in the FSC landscape. However, challenges such as integration complexities, data quality, scalability, and regulatory concerns should be addressed.
Through these challenges, Artificial Intelligence (AI) arises as a potential solution complementing Blockchain. This amalgamation can effectively tackle certain existing obstacles, such as ensuring data accuracy and system compatibility, while providing stronger solutions for food safety and fraud prevention. The implementation of a comprehensive blockchain solution requires strategic collaboration, technological refinement, and regulatory alignment to fully realize its benefits and address the intricate management challenges of traditional FSC information systems.
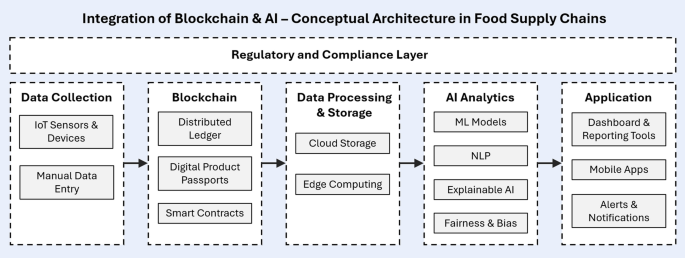
This work not only contributes valuable insights to the academic community but also aligns closely with the ALLIANCE project’s mission to accelerate digital innovation in agri-food systems.
Stay tuned as we continue to explore, innovate, and implement next-generation solutions that can build safer, smarter, and more sustainable food systems for Europe and beyond.
Read the full paper
For further details, the full paper is available (open access) on the BISE Journal's website. Furthermore, it can also be found, together with all the scientific publications related to the ALLIANCE project, on the dedicated page in the Zenodo repository.